Inference Statistics: Parametric VS Non Parametric
Hello Reas Friends, in this modern era we often encounter through various media publications the presenting or analyzing a set of data based on the information they own. Many of them use statistical tools, ranging from simple descriptive statistics to more complex inference statistics. Today, we will provide a simple explanation regarding inference statistics which is generally divided into Parametric and Non Parametric.
As an introduction, we will explain in advance the definition of descriptive statistics. Descriptive statistics are statistical methods used to collect, summarize, present, and decrypt data so that it can provide useful information. Data presented in descriptive statistics are usually in the form of tables, as well as graphs (histograms, pies, and bars), data center measures (mean, median, and mode), data distribution measures (deviation and variance standard).
Now let’s enter the core discussion, Inference Statistics. Inference statistics is a method that deals with data analysis on samples and the results are used to generalize to the population. The use of inference statistics is based on probability and samples obtained randomly.
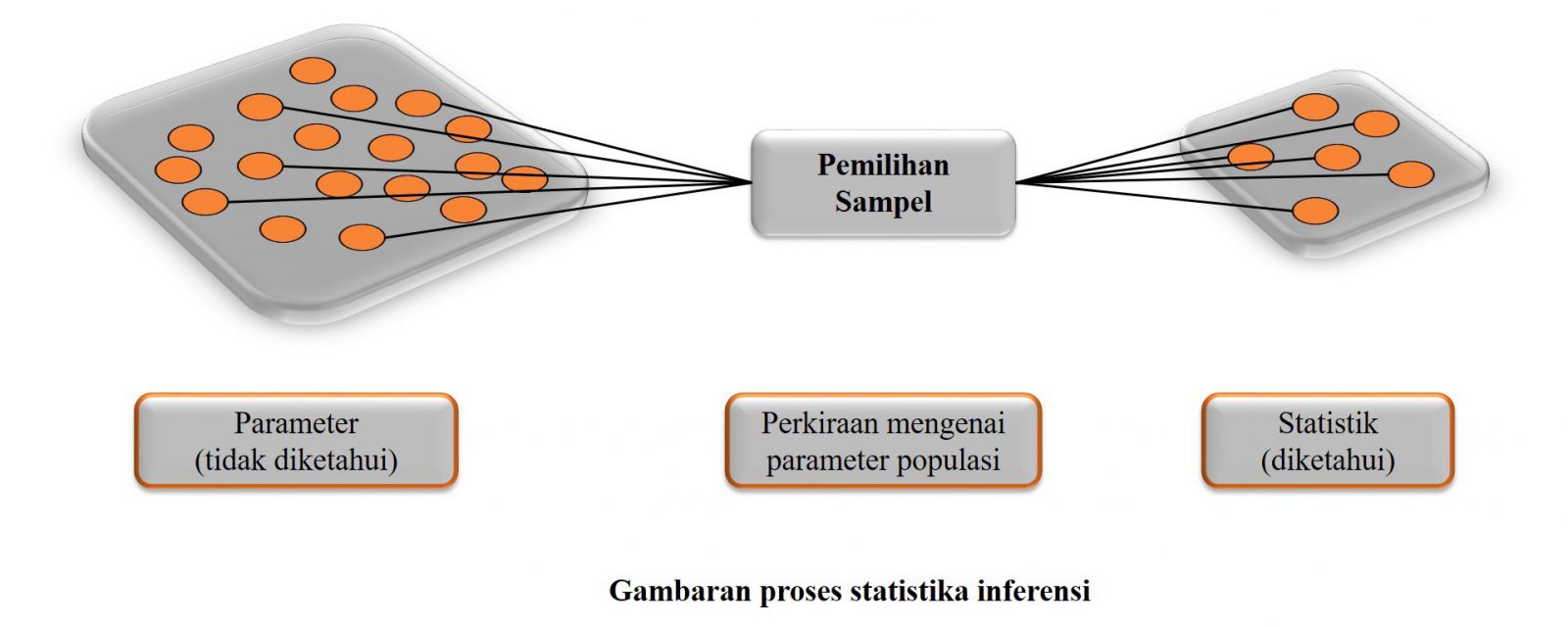
Analysis of the population is a difficult thing to do because besides being very complicated and complex, it is also not time and cost effective. This is the background of inference statistics necessary and important to do. The concept of inference statistics allows the researcher to perform an analysis using data from a sample to estimate an unknown population parameter. Inference Statistics is divided into 2, namely Parametric and Non Parametric.
1. Parametric
It is a statistical inference method whose model determines the existence of certain conditions (assumptions) of the distribution of population data. The application of parametric methods in general is to predict or test unknown parameters from certain distributions that are considered in accordance with data conditions, for example the assumption of normal distribution that must be met in the regression model. In addition, when viewed from the amount of data, it is usually large, at least greater than or equal to 30 data.
2. Non Parametric
The term non-parametric was first used by Wolfowitz, in 1942. Non Parametric statistical methods do not require assumptions about the distribution of population data (data distribution is not known and do not need to be normally distributed). Other terms that are often used for non parametric statistics are distribution free statistics and assumption-free test. Usually, the data used in this method are not that large, less than 30 data.
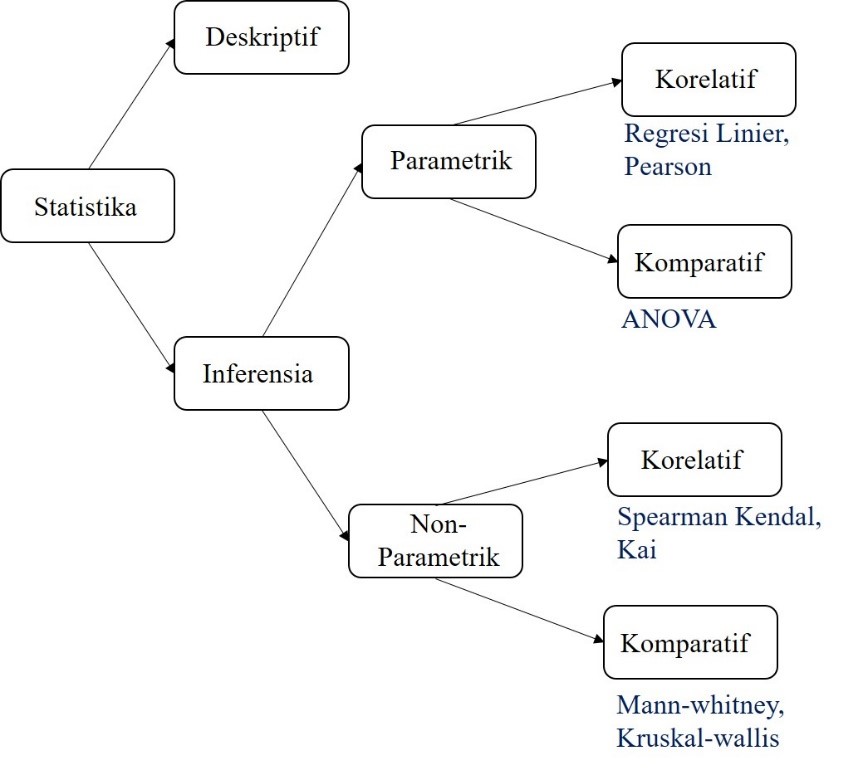
There are several statistical analysis techniques that can be used both for parametric and non parametric:
a) Correlative
Correlative analysis techniques are used to determine the relationship or correlation between one variable and another. For example, in a simple linear regression analysis that looks for the relationship between the dependent variable Y and the independent variable X.
Examples for each method:
• Parametric: Linear regression, Pearson
• Non parametric: Spearman Kendal, Kai
b) Comparative
Comparative analysis techniques are used to determine differences in values (parameters), for example the average of a group with other groups or to find out differences in the retirement age of employees of company A and company B.
Examples for each method:
• Parametric: ANOVA
• Non parametric: Mann-whitney, Kruskal-wallis
To understand, you can see the picture below which is a summary of what has been explained to show the types of statistics and analysis techniques.
Ok, from this explanation, there are those who will wonder, "Is it better to use Parametric or Non Parametric?" , "Which one is easier to use?" Each method has advantages and disadvantages. When viewed from the process, it is non parametric that is simpler and faster, but the results of non parametric statistical hypothesis testing are not as sharp as parametric statistics and sometimes certain information is ignored.
Reference :
https://www.sciencedirect.com/browse/journals-and-books?subject=mathematics
Author





 42214
42214



 20 Dec 2022
20 Dec 2022 10452 kali
10452 kali





