Gas Power Plant (PLTG)
Gas Power Plant (PLTG)
PLTG is a type of generator that uses "hot air" to turn a turbine. This hot air is generated by heating the air using the gas in the combustion chamber. The hot air is then flowed to the turbine. PLTG scheme is shown in Figure 1.
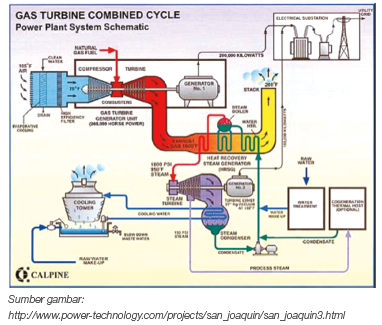
Natural gas power plants tend to have more environmentally friendly emissions than coal-fired power plants. The process of generating electricity using natural gas is quite different from the mechanism in the steam power plant (PLTU). The natural gas combustion process is not used to carry out the heating process like the PLTU but is used directly to turn the turbine. Before going through the combustion process, the air is compressed using a compressor. Then the compressed air is flowed into the combustion chamber to then react with the gas. In this process, the pressure contained in the air and the chemical energy contained in the gas are converted into kinetic energy which is then used to turn the turbine. The advantages and disadvantages of PLTG are summarized in Table 1.
Figure 1. Schematic of a gas turbine
| Advantages |
More efficient |
| Simple construction and smaller required area | |
| Electrical capacity is more varied | |
| More environmentally friendly than PLTU | |
| The speed in response to increased power is higher | |
| Disadvantages |
Usually to only meet peak power |
| Sound pollution |
|
| High operational cost |
Table 1. Advantages and Disadvantages of PLTG
The gas that comes out of the gas turbine still has a high enough temperature. Thus, the hot gas can still be used. One of the uses of hot gas is to heat the working fluid used in the PLTU, through a device called Heat Recovery Steam Generator (HRSG). The combination of gas turbines and steam turbines in electricity generation is known as PLTGU (Gas and Steam Power Plants). PLTGU has higher efficiency compared to PLTU and PLTG, considering that there is less energy that is not utilized. T
| Advantages |
More efficient compared to PLTG |
| Lower operational cost compared to PLTG |
|
| Earlier starting time |
|
| More simple maintenance procedure | |
| Disadvantages |
Needs at least two kinds of fuel |
| Shorter lifetime |
The advantages and disadvantages of PLTGU are shown in Table 2.
Author





 142291
142291



 15 Mar 2022
15 Mar 2022 7347 kali
7347 kali





